Photo by Patrick Hendry on Unsplash
Industry 4.0 Synopsis - New Gen Technology Convergence & Architectural Constructs
This article is more of collation of various different artefacts and architectural diagrams which should serve as one stop solution for introduction on Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is changing the way businesses make, improve, and distribute their goods. Manufacturers are incorporating new technology into their manufacturing facilities and processes, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing and analytics, and AI and machine learning.
Advanced sensors, embedded software, and robotics are used in these smart factories to collect and analyse data, allowing for better decision-making. When data from manufacturing operations is coupled with operational data from ERP, supply chain, customer service, and other enterprise systems, new levels of visibility and insight are created from previously isolated data.
Increased automation, predictive maintenance, self-optimization of process improvements, and, most importantly, a new level of efficiency and responsiveness to consumers not before feasible are all benefits of digital technologies.
The manufacturing industry has a fantastic potential to enter the fourth industrial revolution by developing smart factories. Analyzing vast volumes of big data received from factory sensors ensures real-time view of manufacturing assets and can provide tools for performing predictive maintenance to reduce downtime.
Smart factories that use high-tech IoT devices have higher production and better quality. Using AI-powered visual insights to replace manual inspection business models decreases manufacturing errors and saves money and time. Quality control staff can set up a smartphone connected to the cloud with minimal expense to monitor manufacturing operations from nearly anywhere. Manufacturers can spot mistakes sooner rather than later, when repair work is more expensive, by using machine learning algorithms.
The concepts and technologies of Industry 4.0 can be used in a variety of industries, including discrete and process manufacturing, as well as oil and gas, mining, and other sectors.
Industry Evolution Timeline
The first industrial revolution, which began in the late 18th century in Britain, enabled widespread production by utilising water and steam power instead of solely human and animal power. Rather than meticulously producing products by hand, finished goods were constructed with machines.
The second industrial revolution, which began a century later, brought assembly lines and the utilisation of oil, gas, and electricity. These new power sources, combined with more advanced communications via telephone and telegraph, enabled manufacturing processes to achieve mass output and some automation.
Computers, modern telecommunications, and data analysis were introduced to manufacturing processes during the third industrial revolution, which began in the middle of the twentieth century. Embedding programmable logic controllers (PLCs) into machinery to assist automate some operations and gather and exchange data was the first step in the digitalization of industries.
The fourth industrial revolution, commonly known as Industry 4.0, is now underway. Informed data helps to manufacture things more effectively and productively across the value chain, as seen by increased automation and the use of smart equipment and smart factories. Manufacturers' flexibility is enhanced so that they may better satisfy consumer expectations through mass customisation, eventually aiming for efficiency with a lot size of one in many circumstances. A smart factory may achieve information transparency and better judgments by gathering more data from the manufacturing floor and linking it with other company operating data.
Characteristics
- Data analysis for optimal decision making
- IT-OT integration
- Custom manufacturing
- Supply chain
Core Technologies of Industry 4.0
- Internet of Things (IoT)
Here I would provide architecture considered in different cloud hyperscalers:
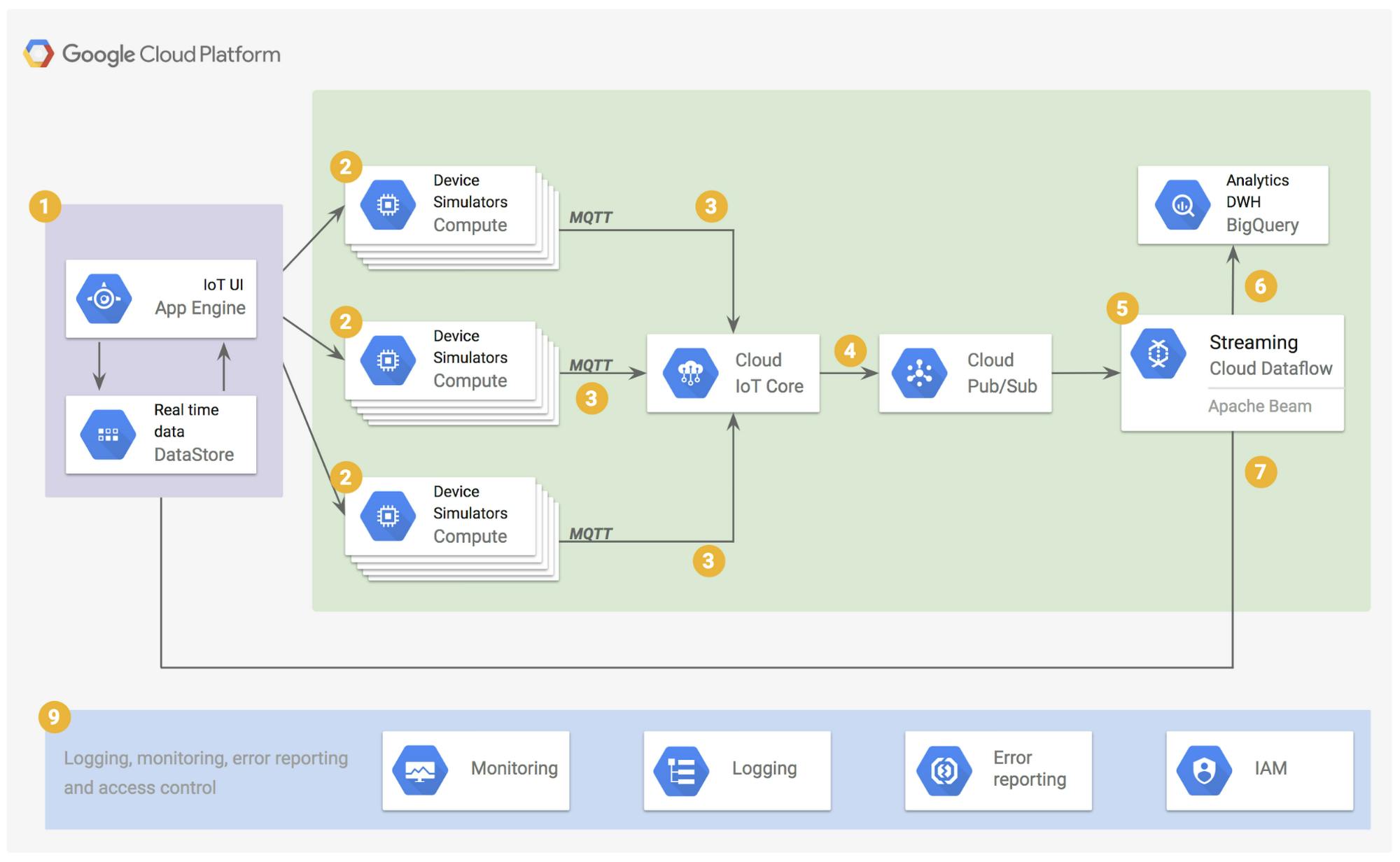
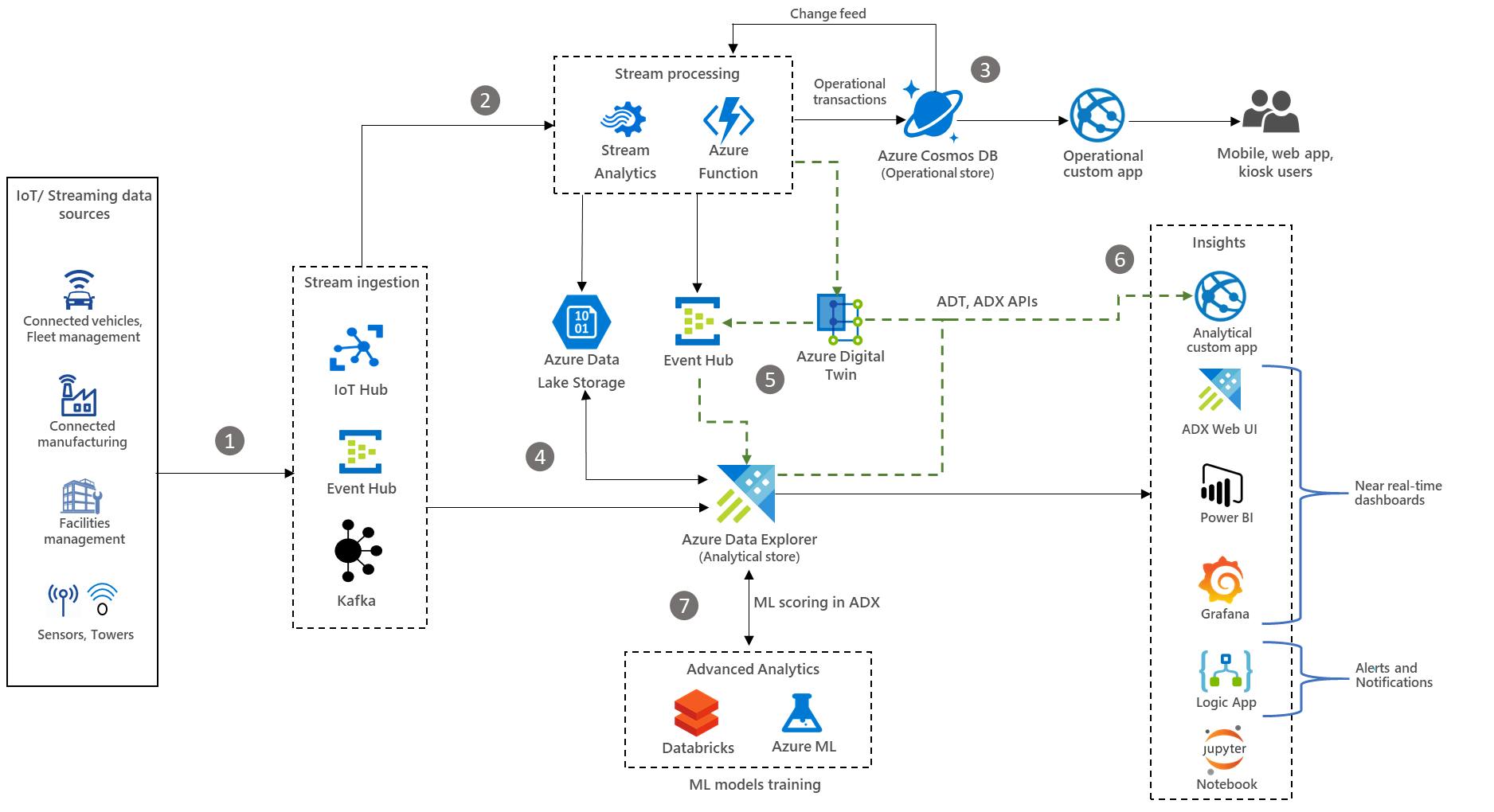
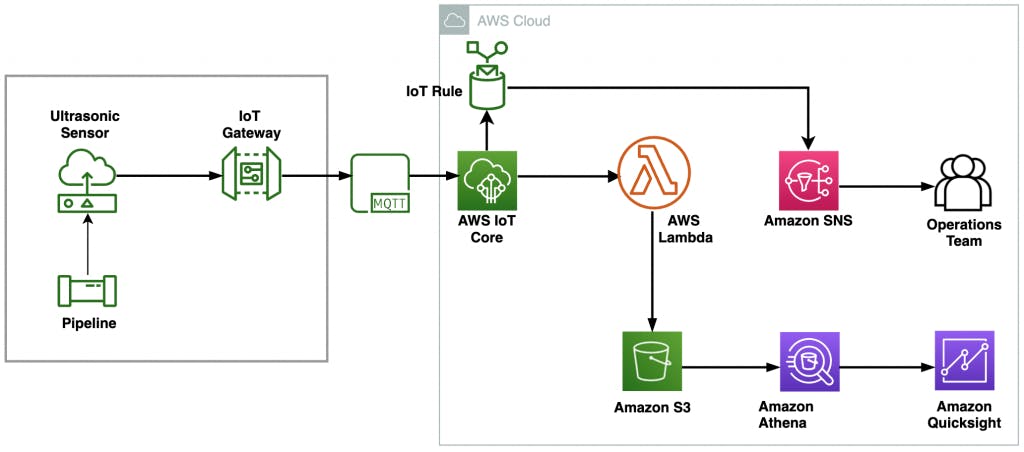
- Digital Twins
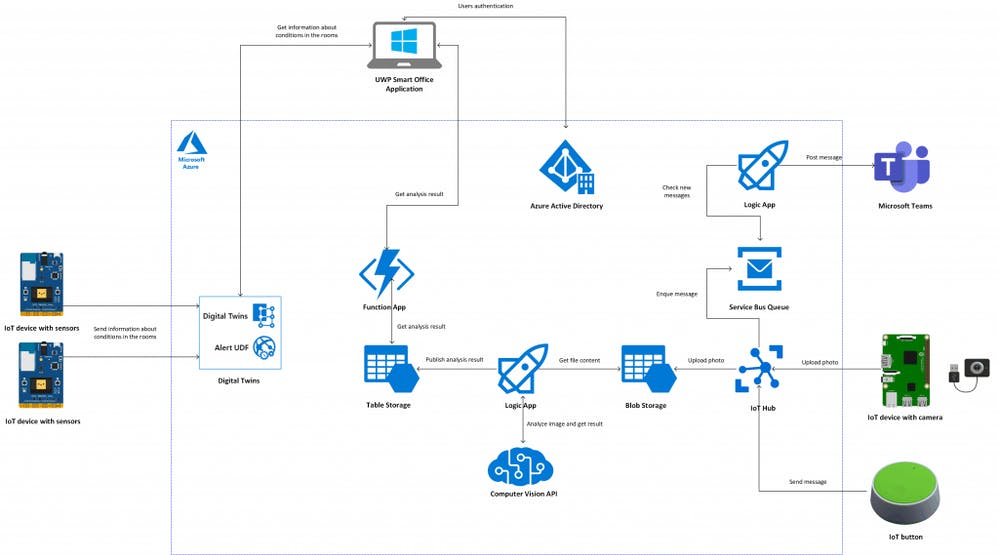
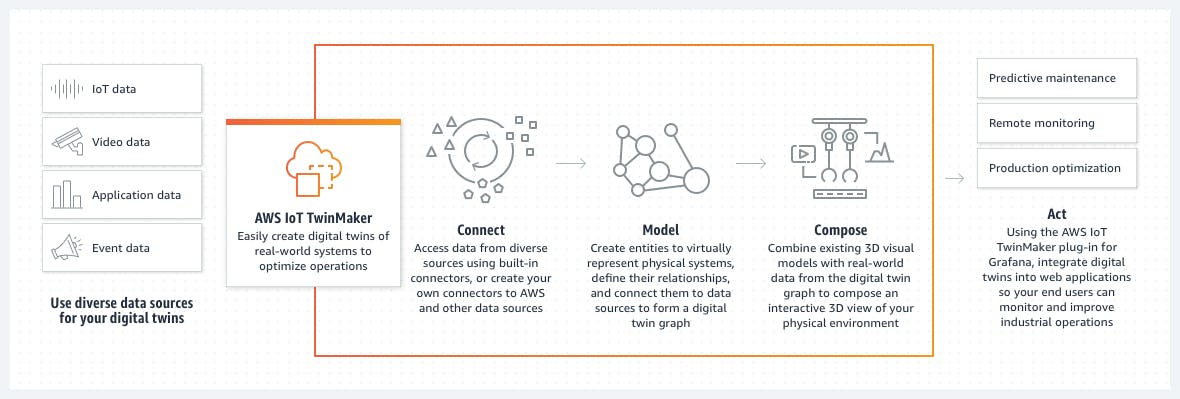
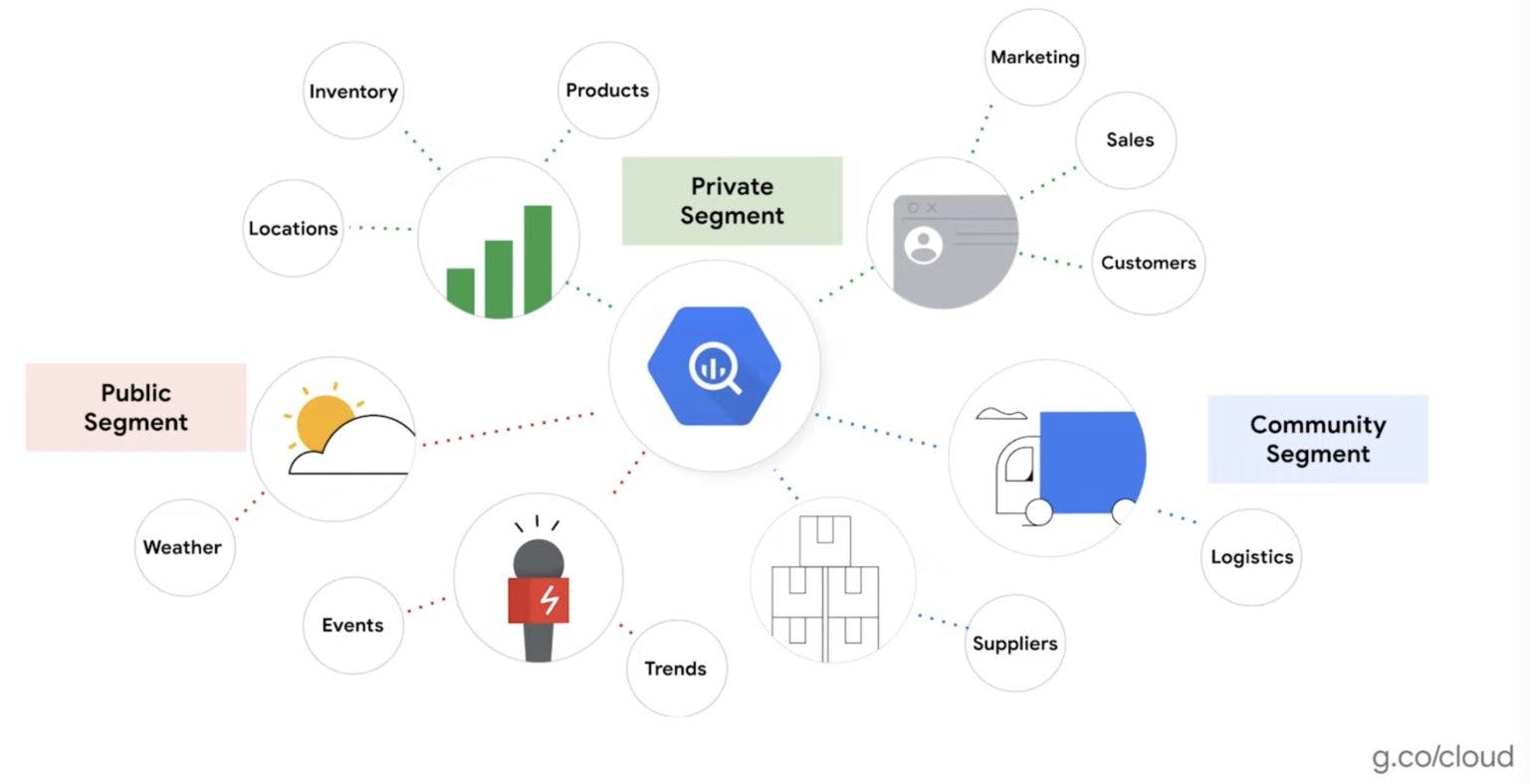
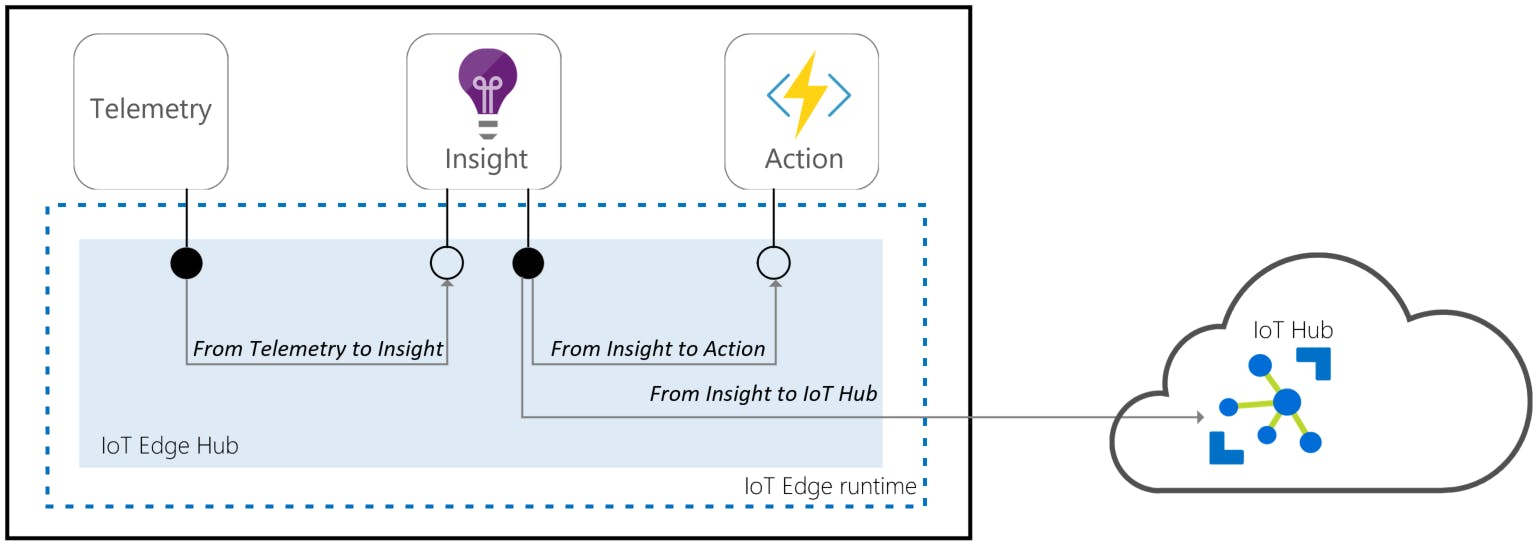
- Edge Computing
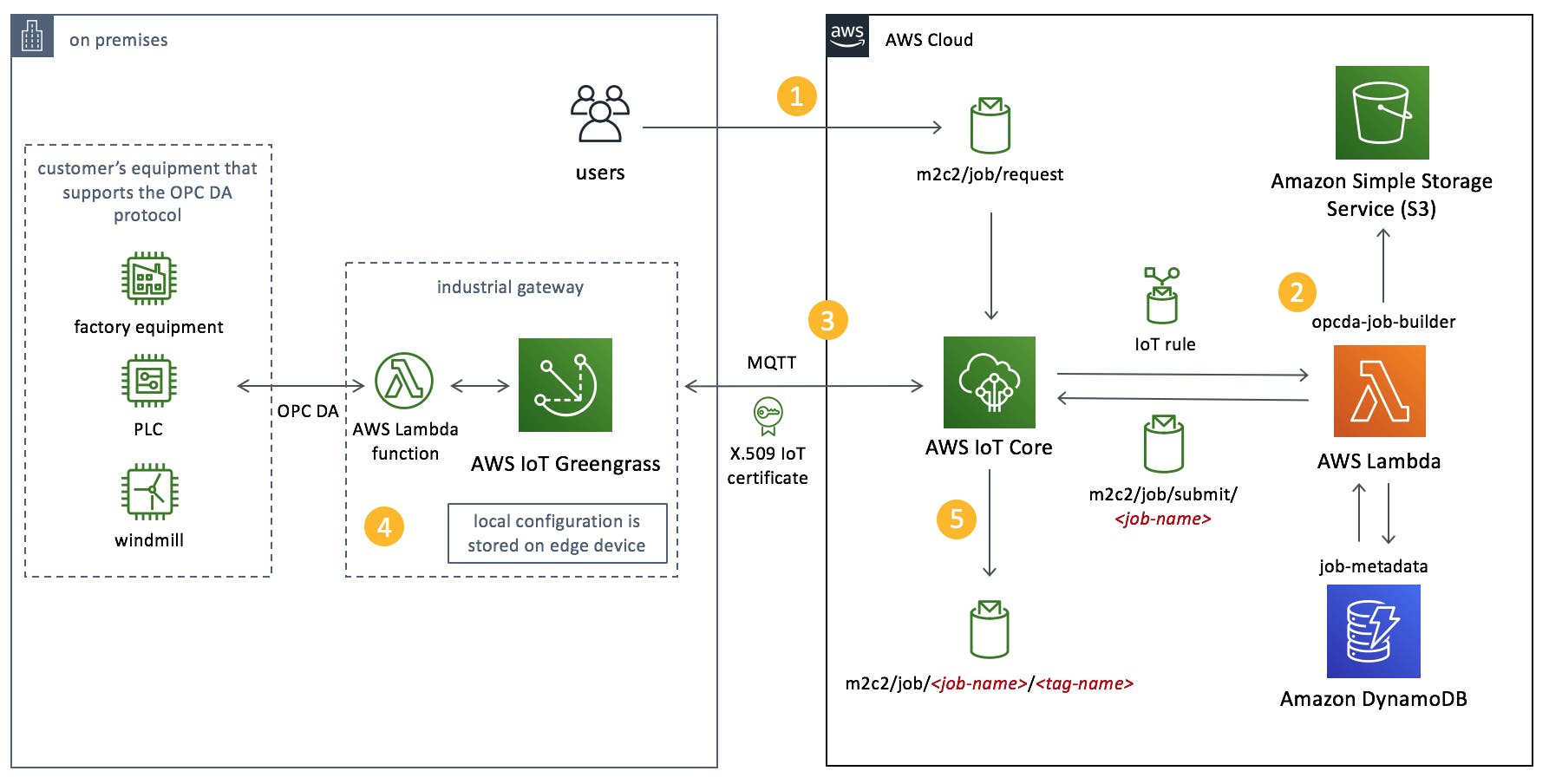
- Cyber Security
- Cloud Computing
References:
- ibm.com/in-en/topics/industry-4-0
- beyondplm.com/2021/09/14/google-product-dat..
- azure.microsoft.com/en-in/services/iot-edge
- aws.amazon.com/iot/solutions/mli-accelerator
- techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/azure-iot/sm..
- aws.amazon.com/iot-twinmaker
- techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/azure-iot/sm..
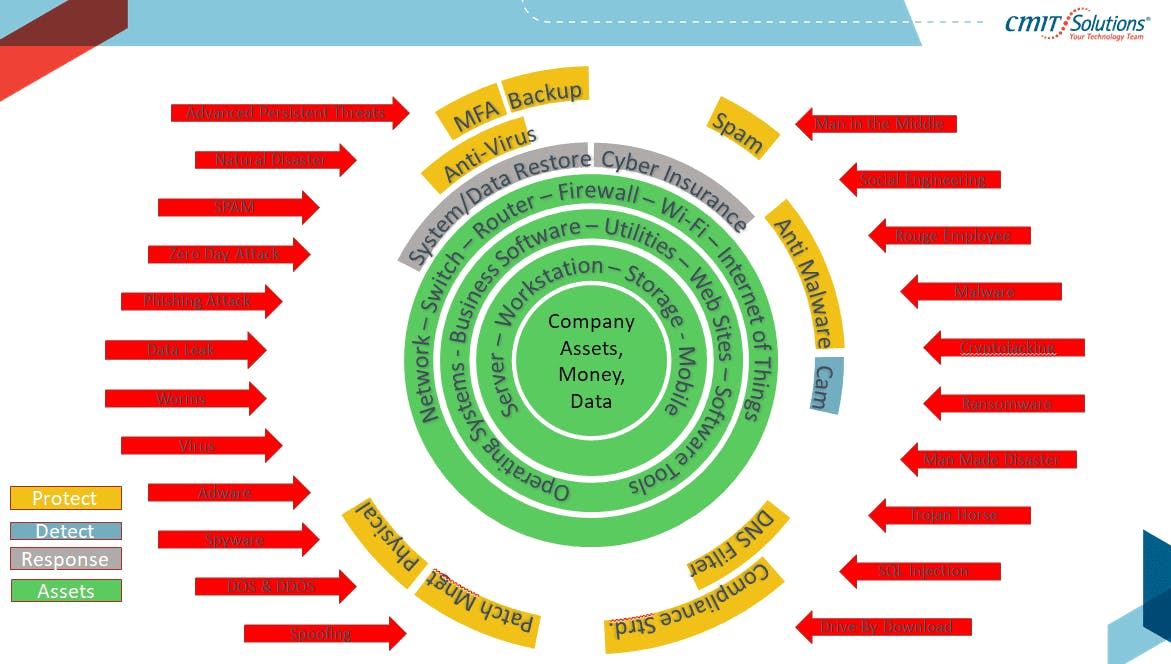
- cmitsolutions.com/round-rock/?p=5626
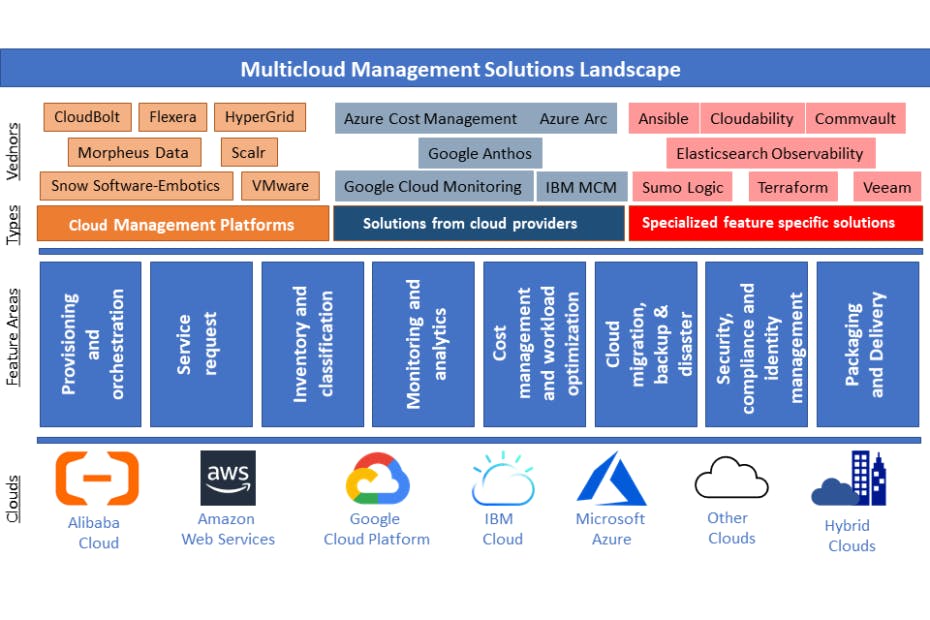
- narangsanjay.com/blog/multicloud-management..

